|
|
Liver Trauma
Hepatic Laceration
- Most frequently injured abdominal organ
after spleen
- Most often due to deceleration injuries
- Often seen in association with
- Right-sided rib fractures
- Right-sided pneumothorax
- Right lung contusion
- Injuries to the right kidney or
adrenal gland
- Injuries include
- Subcapsular hematoma
- Laceration
- Intrahepatic hematoma
- Contusion
- Right lobe more often injured than left
- Injury to left lobe associated with
injury to duodenum, pancreas, transverse colon
- More often due to direct blows to
the epigastrium
- High association with injuries to other
organs
- 45% with liver injuries have splenic
injury
- Subcapsular hematomas
- Lenticular configuration
- Flattens adjacent liver
- Often adjacent to rib fracture
- Most occur in antero-lateral aspect of
right lobe
- Liver Laceration
- Non-enhancing region, linear or
branching
- Frequently parallel hepatic vein
- Hypodense wedge extending to liver
surface
- Focal hepatic devascularization
- Periportal tracking of blood
- Frequent finding
- Sometimes only evidence of injury
- Due to dissecting hemorrhage
- Bile
- Dilated periportal lymphatics
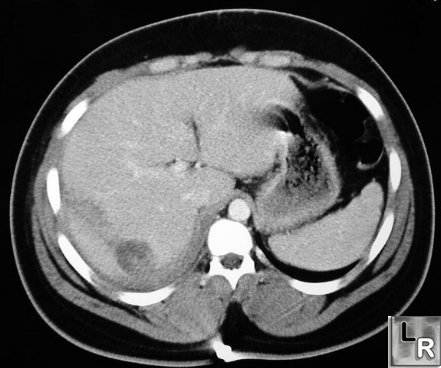
Liver Laceration. Contrast-enhanced CT of abdomen shows linear
low-attenuation defect
crossing the posterior aspect of the right lobe of the liver representing a
laceration
- Hematoma
- Higher attenuation than surrounding
liver on unenhanced CT scan
- Lower attenuation than surrounding
liver on enhanced CT scan
- Central high attenuation region
containing clot
- Hepatic vein laceration usually
involves right hepatic vein near vena cava
- Contusion
- Rare lesions
- Low attenuation area compared to
normally enhanced liver
- Do not disrupt major portal or hepatic
venous structures
- Hemoperitoneum
- Complications
- Delayed rupture (rare)
- Hemobilia
- Arteriovenous fistula
- Pseudoaneurysm
- Biloma
- Superinfection of hematoma
- Pitfalls
- Adjacent rib artifacts-beam-hardening
- Mimics laceration
- Adjacent to ribs
- Fade as they become farther from
rib
- Linear artifact from air-contrast
level in stomach
- Fatty liver with laceration or
hematoma can be missed
- Clue- look at intrahepatic ducts and
vessels
- Treatment
- Conservative treatment in up to 80% in
adults and almost all children
- Monitor hemodynamic state of patient
- Transcatheter embolization possible
for bleeders
- Healing
- Contusions may clear in 5-7 days
- Subcapsular hematomas may increase
in size initially before clearing
- Lacerations can heal within weeks
but small, residual bilomas are common
|
|
|